Learn About Health Insurance in Your State!
The Cost of Health Insurance in the United States
The average cost of health insurance in the United States is $6,981 per person based on the most recently published data. For a family of four this translates to $27,924 per year. This cost varies significantly by state and by type of insurance. The map below identifies the health insurance cost, by state.
WANT MORE INFO ON HEALTH INSURANCE IN YOUR STATE?
- Lowest Priced States
- Medium Priced States
- Highest Priced States
Click your state for more information on health insurance prices
US Insurance Cost by Type of Insurance
Health insurance costs vary significantly based on the population insured. The chart below shows the cost per person of the four major insurance types. The dollar amount is the average cost to insure people for each type of insurance.
United States Health Insurance Cost Per Person
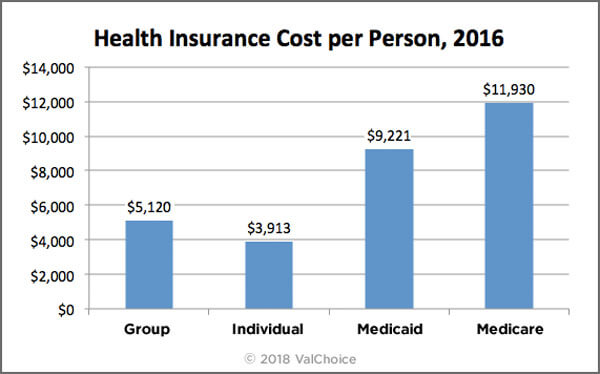
Average cost calculations for comprehensive group and individual insurance is based on data reported to state insurance departments. Group insurance is based on 44,878,149 enrollees and Individual insurance is based on 15,854,371. Supplementary vision and dental insurance contracts sold as riders to comprehensive insurance are not included. Medicaid costs are based on cost data from Macpac.gov divided by the number of people covered based on Kaiser Family Foundation data. Medicaid data includes both state and federal spending. Medicare costs are based on data from CMS.gov divided by the number of people covered based on Kaiser Family Foundation data. CMS cost data are from 2014, adjusted for health insurance cost inflation rates.
Number of People Covered by Health Insurance in the US
The chart below shows the number of people insured with each type of insurance plan available. The most recent reported year plus three years of history is shown. The key takeaways shows in this chart are that the number of people covered by group health insurance is relatively flat, with a slight increase. The number of people covered by other types of insurance are all increasing much more rapidly than the growth rate in group coverage.
Number of People Covered by Type of Health Insurance
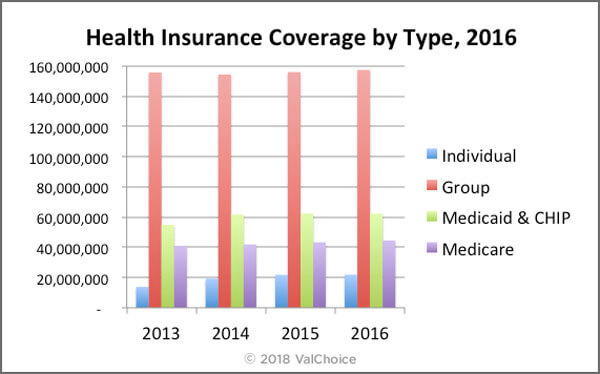 Data from the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Data from the Kaiser Family Foundation.
How Patients Use Health Care Services
The tables below show the frequency with which residents use different types of health care services. The data is collected from insurance company filings with state insurance departments. The number of enrollees on which data was collected is as follows: Group insurance 44,878,149, Individual insurance 15,854,371, Medicaid managed care 47,904,368 and Medicare Advantage 16,0636,412.
Doctor Visits, Per Person, Per Year by Insurance Type
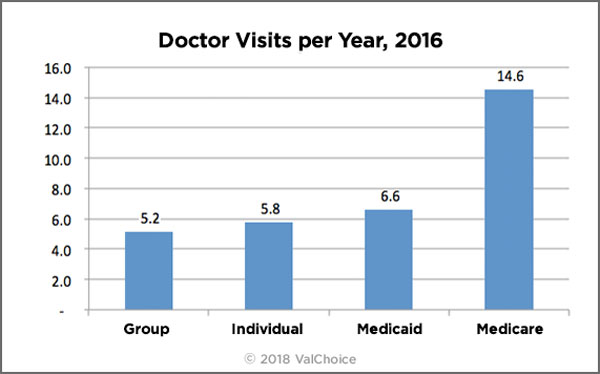
Doctor visits per year includes visits to doctors in which the patient had not been admitted into an institution such as a hospital.
Frequency of Using Medical Services Other Than a Doctor or Hospital 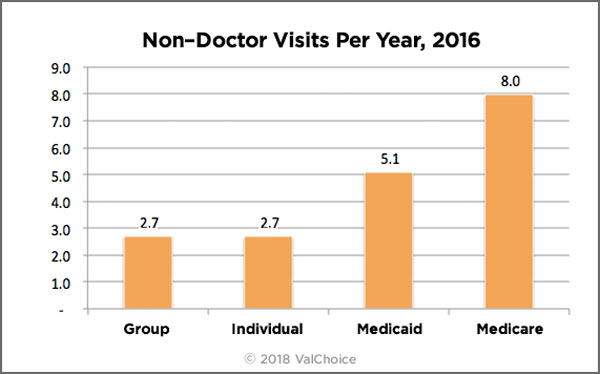
Non-doctor health care visits is a measure of how often people receive medical care without seeing a doctor. This type of care excludes patients that have been admitted to hospitals or other institutions. Examples of non-physician health care includes appointments or walk-in clinics to see a nurse, physical therapist, mental health appointments or other non-physician medical personnel.
Average Number of Days Insured People Spent in the Hospital
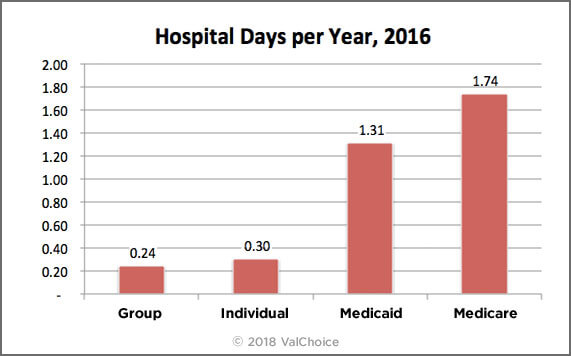
The number of days in the hospital are counted starting with the day the patient is admitted. The last day is not counted, unless the first and last day are the same day.
Medicaid Expansion
The expansion of Medicaid is a major topic at both the state and federal level. The map below shows the states that have already enacted Medicaid expansion and those where Medicaid expansion has not yet been embraced. Below the map are charts comparing the cost of various types of insurance in these two categories of states.
- Medicaid Expansion
- No Medicaid Expansion
Data Source: Kaiser Family Foundation
Health Insurance Cost Comparisons
The charts below compare the cost of health insurance for the four primary insurance types. The costs are grouped into states that have and have not embraced Medicaid expansion. The color coding on the charts below matches the color coding of the map above.
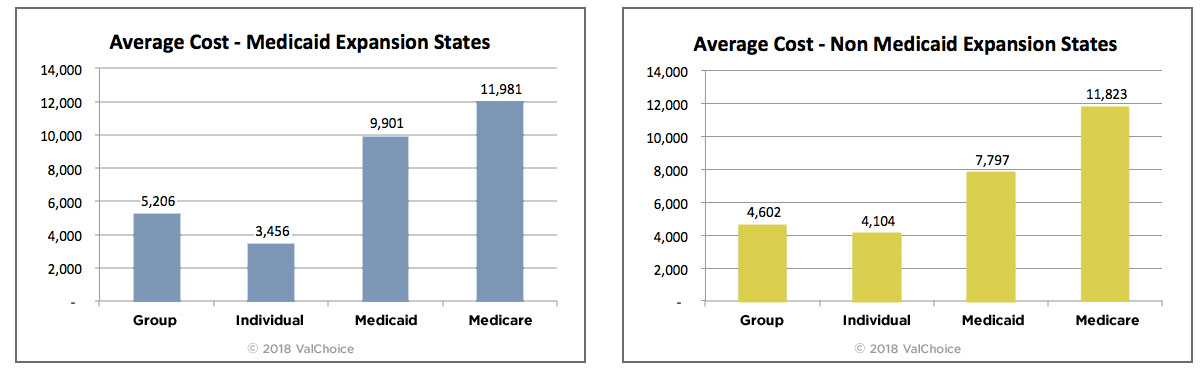
Average cost calculations for comprehensive group and individual insurance is based on data reported to state insurance departments. Supplementary vision and dental contracts sold as riders to comprehensive insurance are not included. Medicaid costs are based on data from Macpac.gov and include state, federal and individual spending. Medicare costs are based on data from CMS.gov. CMS data are from 2014, adjusted for health insurance cost inflation rates.
The Effect of Insurance Deductibles on The Cost of Health Care
NH residents insured through group, individual and medicare health plans generally have a deductible. Deductibles define the amount of the medical expenses the insured person must pay before the insurers coverage begins to pay the medical bills. The deductible amount depends on the insurance plan. Generally speaking, individual insurance has larger deductibles than other plans. Deductibles have the effect of increasing the cost of the insurance for people that file insurance claims. For example, a person on an individual plan paying the average price of $3,856 with a relatively common $6,000 deductible has an effective price of nearly $10,000, if they use their insurance.
Overview of The Different Types of Health Insurance Plans
Individual Coverage
The individual health plan is for people who do not qualify for other types of insurance. This type of insurance is often referred to as Obamacare or the Affordable Care Act (ACA). Self-employed and unemployed people who are not eligible for employer provided insurance often purchase individual coverage. The premiums earned under this type of insurance are based on the premiums paid by the individual. Tax credits provided to make the insurance affordable are not included in the premiums earned. Individual coverage includes all types of plans. The basic plan types are referred to as Bronze, Silver and Gold Plans.
Group Coverage, Also Known as Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
Companies that provide health insurance to employees as a benefit provide an insurance type known as group insurance. The cost of this type of health plan is based on total premiums paid to the insurance company. Premiums include payments from both employers and employees. Premiums do not include payments for services such as deductibles, co-pays or other out-of-pocket costs. Group coverage includes: Health Maintenance Organizations (HMO), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPO), Point-of-Service (POS) Plans and High-Deductible Health Plans.
Medicaid and CHIP
Medicaid total cost and enrollment numbers include the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP). These programs provide health insurance coverage that is not included under Medicare coverage. Examples of the type of health coverage provided includes doctor visits, hospital expenses, nursing home care and home health care. Medicaid also covers long-term care costs, both in a nursing home and at-home care. The costs associated with medicaid is inclusive of both state and federal spending.
The data on how Medicaid patients use health services is based on Medicaid managed care. Medicaid managed care provides for the delivery of Medicaid health benefits and additional services through contracted arrangements between state Medicaid agencies and managed care organizations (MCOs) that accept a set per member per month (capitation) payment for these services. The capitation model is unique in that it is not a pay for service. Instead, this is a set fee paid per member, per month, whether or not the person seeks service.
Medicare and Medicare Advantage
The charts showing the cost the the number of enrollees includes people covered by all types of Medicare and Medicare Advantage. The cost of this type of health coverage includes participation from employers, individuals, federal, state and local government. Excluded from the costs are any form of co-pay or a deductible the individual must pay to receive care.
How enrollees use their health care services is based on enrollees in Medicare Advantage plans only. Medicare Advantage plans are Medicare health plans offered by private companies that contract with Medicare. Medicare Advantage plans include Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), Private Fee for Service Plans, Special Needs Plans and Medicare Medical Savings Account Plans (MMSAPs).
Auto and Homeowners Insurance in the US
Learn which companies offer the best auto and homeowners insurance in the state where you live by clicking the following link:
Links to Information on Health Insurance in Your State
Clicking the maps above, or the links below, will take you to more detailed information on health insurance in your state.
Alaska
Arizona
Arkansas
California
Colorado
Connecticut
Delaware
District of Columbia
Florida
Georgia
Hawaii
Idaho
Illinois
Indiana
Iowa
Kansas
